Active Transport
Active Transport Revision
What is Active Transport?
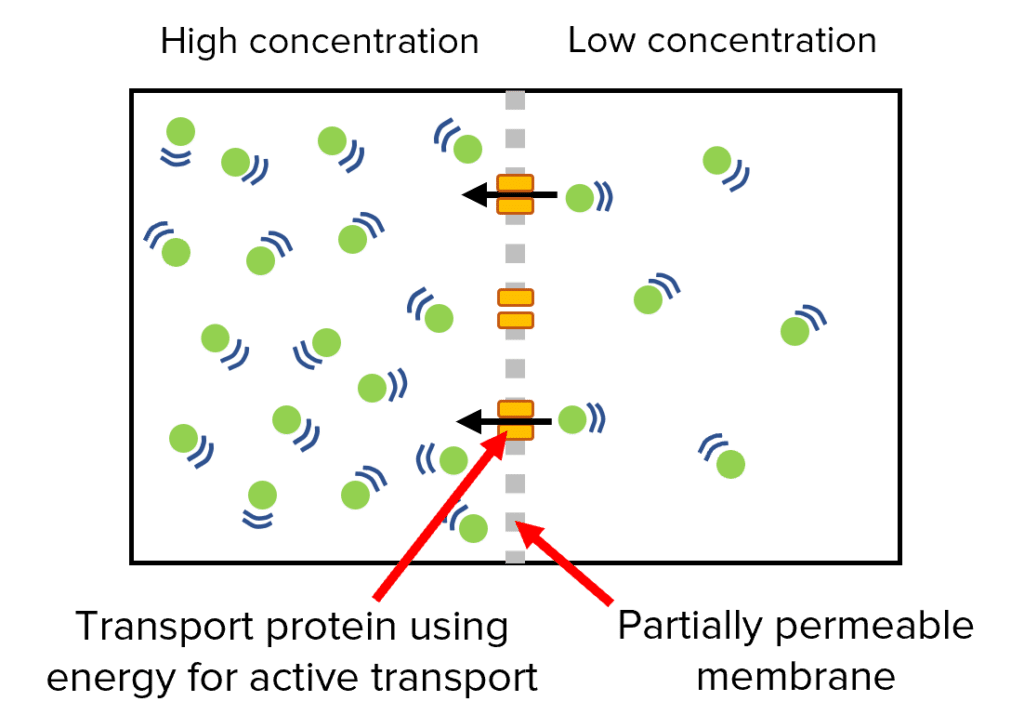
Active transport allows substances to travel from an area of low concentration to high concentration, against the concentration gradient.
It requires energy from respiration to do this.
Transport proteins on cell membranes use the energy to move substances against the concentration gradient.
Examples of Active Transport
Root hair cells are specialised cells that create an exchange surface with the soil. They uptake the water and mineral ions needed for plant growth. When the soil mineral solution is dilute and there is a higher concentration of mineral ions inside the root hair cells, the minerals will not passively diffuse in. Root hair cells use energy from respiration to actively transport the ions against the concentration gradient and into the cell.
Humans sometimes use active transport to absorb nutrients (such as amino acids and glucose) from the small intestine. If the concentration of nutrients in the intestinal cells is higher than the concentration of nutrients in the small intestine, they can’t diffuse across passively. Active transport allows nutrients to be absorbed into the walls of the intestine against the concentration gradient so they can enter the blood and can be transported around the body to be used for respiration.
Comparing Transport Processes
You need to be able to compare the different transport methods covered so far, diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
|
Transport process |
Direction of flow |
Requires energy? |
Examples |
|
Diffusion |
From high concentration to low concentration, down the concentration gradient. |
No – it is a passive process. |
•Carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange in lungs, fish gills and respiring cell membranes. •Food particles (e.g. glucose and amino acids) from the small intestine into intestinal cells and blood. •Waste substances (e.g. urea) from cells into the blood. |
|
Osmosis |
From high concentration to low concentration, down the concentration gradient. |
No – it is a passive process. |
•Water in and out of cells. |
|
Active transport |
From low concentration to high concentration, against the concentration gradient. |
Yes – used to go against concentration gradient. |
•Mineral ions into plant root hair cells. •Food particles from small intestine into the intestinal cells when concentration is higher in intestinal cells than the gut. |
Active Transport Example Questions
Question 1: Explain the different ways food molecules, such as glucose and amino acids, are absorbed from the small intestine.
[4 marks]
If the concentration of the nutrients is lower in the intestinal wall cells/blood than in the small intestine then the food molecules move in by diffusion, down the concentration gradient.
If the concentration of the nutrients is higher in the intestinal wall cells/blood than in the small intestine then the food molecules move in by active transport, up the concentration gradient, using energy.
Question 2: How does active transport differ to diffusion and osmosis?
[2 marks]
Any 2 from:
- Active transport moves substances from an area of low concentration to high concentration (against the concentration gradient), whereas diffusion and osmosis move substances from areas of high concentration to low concentration (down the concentration gradient).
- Active transport requires energy but diffusion and osmosis are passive processes (do not require energy).
- Active transport requires carrier proteins to move substances across the membrane but diffusion and osmosis do not.
Question 3: How does osmosis differ to diffusion and active transport?
[1 mark]
Osmosis only describes the movement of water but diffusion and active transport involve the movement of many different molecules.
Active Transport Worksheet and Example Questions
Active Transport Questions
GCSEOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now




