Cell Structure
Cell Structure Revision
Cell Structure
Cells are the basic unit of all living organisms. Many different types of cells can be found within one organism, all with specific subcellular structures that enable them to perform their individual roles.
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic
Cells can be classified into two groups depending on whether they contain a nucleus.
Cells that have a nucleus, such as plant and animal cells, are called eukaryotic cells and cells without a nucleus, such as bacteria, are called prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells tend to be much simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells.
Organisms made up of eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes and organisms that are prokaryotic are called prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes are often multicellular (made up of many cells) whereas prokaryotes are often single-celled (only one cell).
Animal Cell Structure
Animal cells all contain the same subcellular structures:
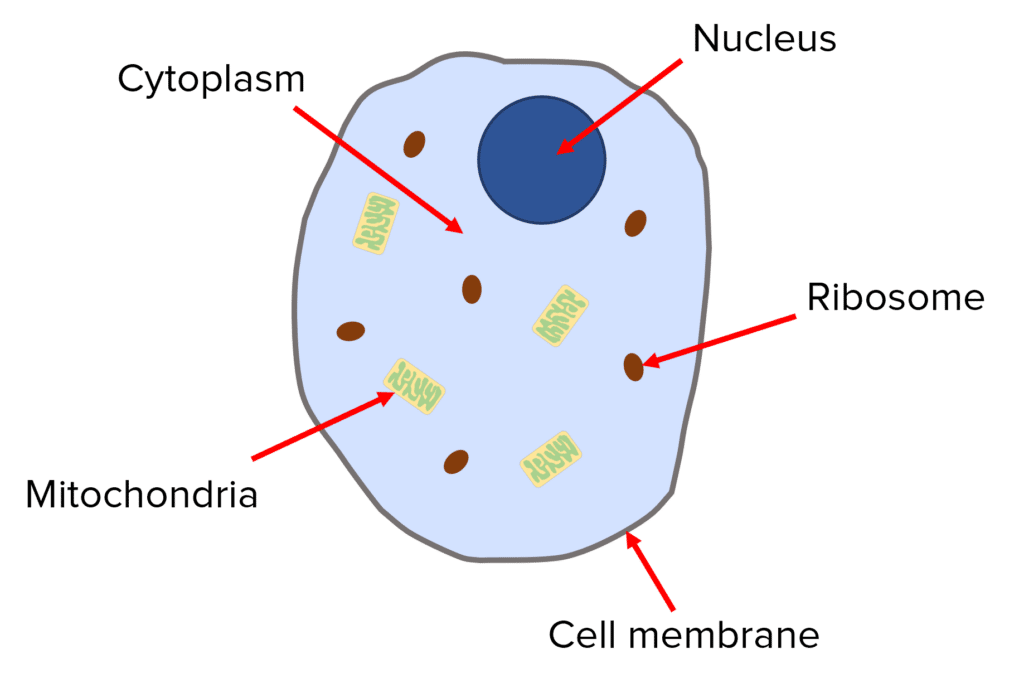
- A nucleus that holds all the genetic material (including DNA) needed to control the cell’s activities.
- Cytoplasm which is a jelly-like substance that contains nutrients, salts and enzymes required for chemical reactions to take place.
- A semi-permeable cell membrane that controls what comes in and out of the cell.
- Many mitochondria that contain enzymes needed for respiration, which releases energy for the cell to use.
- Ribosomes for the production of proteins.
Plant Cell Structure

Plant cells contain the same features as animal cells but they also have:
- A cell wall made of cellulose that provides structure and protection to the cell. Algal cells also have this feature.
- A vacuole that a holds weak solution of sugar and salts called cell sap that keeps the cell swollen.
- Many chloroplasts that are the site of photosynthesis in the cell. They contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs the light and specific enzymes required for photosynthesis to occur and food to be produced.
Bacterial Cell Structure
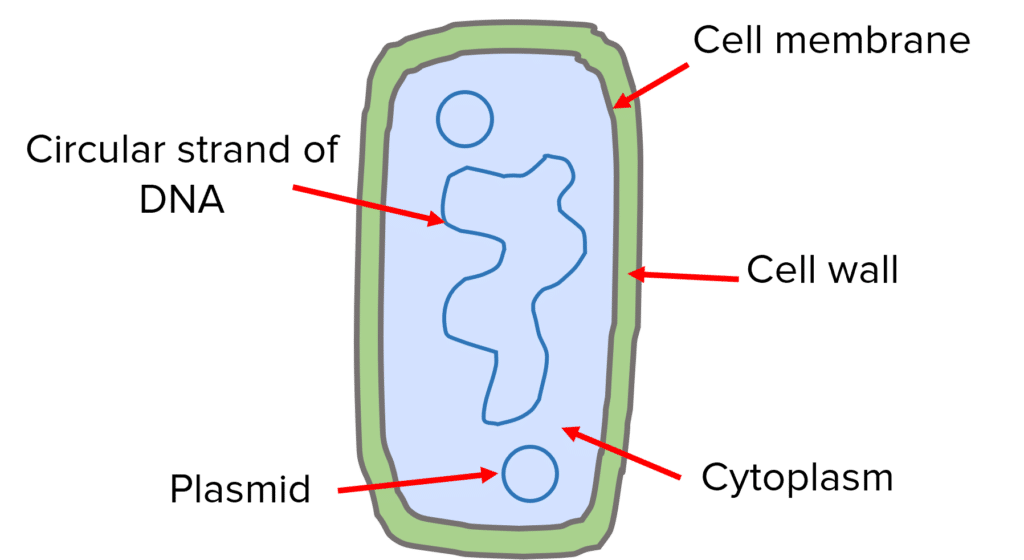
As bacteria do not have a nucleus (prokaryotic), their genetic material is free in the cytoplasm. They have a main circular strand of DNA and occasionally additional small rings of DNA called plasmids.
Bacteria do not contain chloroplasts or mitochondria but do have a cell wall, cell membrane and cytoplasm.
Bacteria often have flagella, hair-like structures that help the bacteria move.
Cell Structure Example Questions
Question 1: What does it mean if a cell is described as ‘prokaryotic’?
[1 mark]
Prokaryotic cells do not contain a nucleus
Question 2: Name 3 features of plant cells that are not also present in bacterial cells.
[3 marks]
Nucleus, Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
Question 3: What is the function of the mitochondria?
[1 mark]
The mitochondria are where respiration takes place which produces energy for the cell to use.






