Digestive Enzymes
Digestive Enzymes Revision
Digestive Enzymes
Enzymes are particularly important in the human digestive system. They break down large food molecules, like carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, into smaller ones so they can be absorbed into the blood and transported around the body.
Purpose of Digestive Enzymes
Food is made up of big molecules such as starch, proteins and fats. They are too big to pass through the walls of the small intestine and be absorbed into the blood, therefore, we must digest them first. This is done by digestive enzymes such as carbohydrases, proteases and lipases.
The body needs to be able to absorb nutrients from food so they can be used to make new carbohydrates, proteins and lipids.
Glucose is a product of carbohydrate digestion and is used to produce energy in aerobic respiration.
Carbohydrases
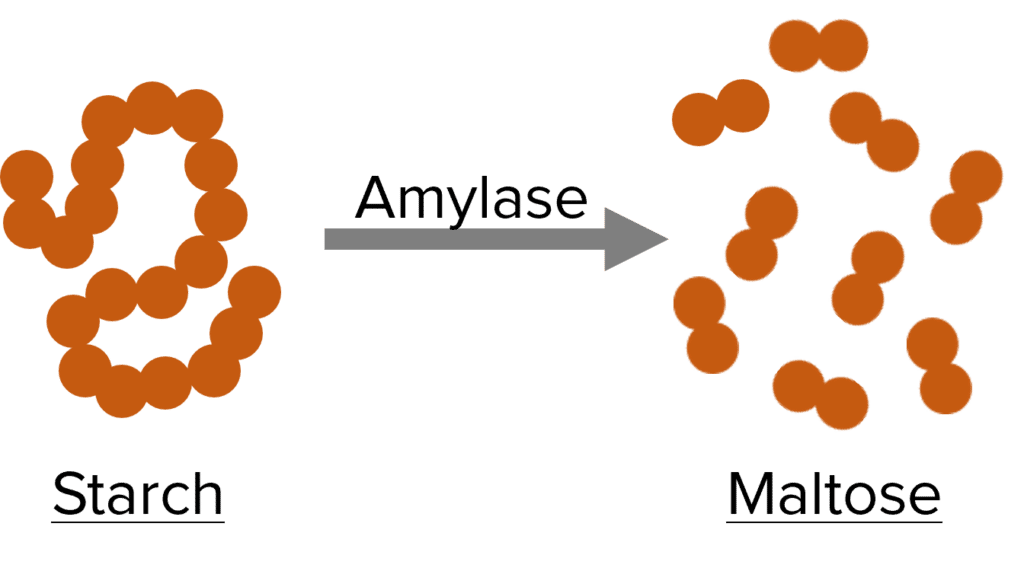
Carbohydrases are digestive enzymes that break down carbohydrates into simple sugars.
Starch is a common carbohydrate in the human diet. It is made up of glucose molecules joined together.
Amylase is a carbohydrase that breaks down starch into maltose (comprised of two glucose molecules).
Amylase digests starch in the mouth and small intestine. It is produced in the salivary glands, pancreas and small intestine.
Proteases
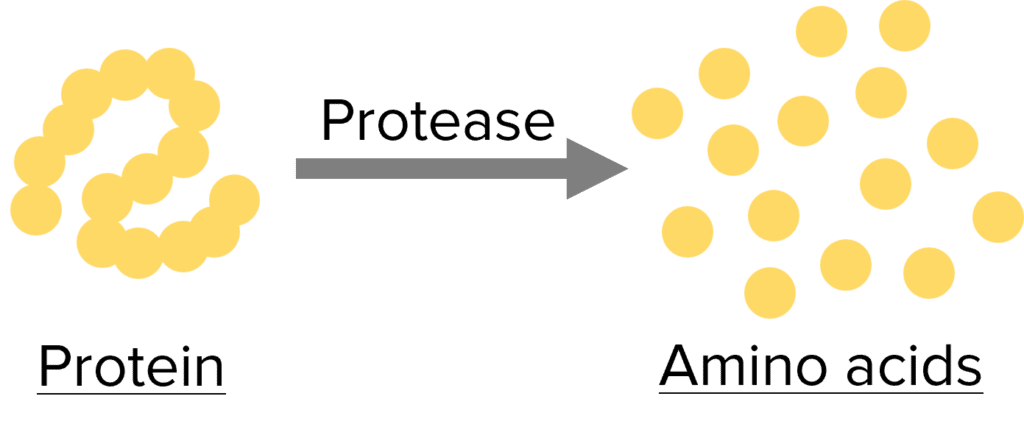
Proteases are digestive enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids.
Proteins are digested in the stomach by pepsin and in the small intestine by other proteases.
Proteases are produced in the stomach, pancreas and small intestine.
Bile and Lipases
The digestion of lipids (fats) is a 2 step process. First they get emulsified by bile, then they get broken down by lipases.
Bile is produced by the liver, stored in the gall bladder and then released into the small intestine. It has 2 uses:
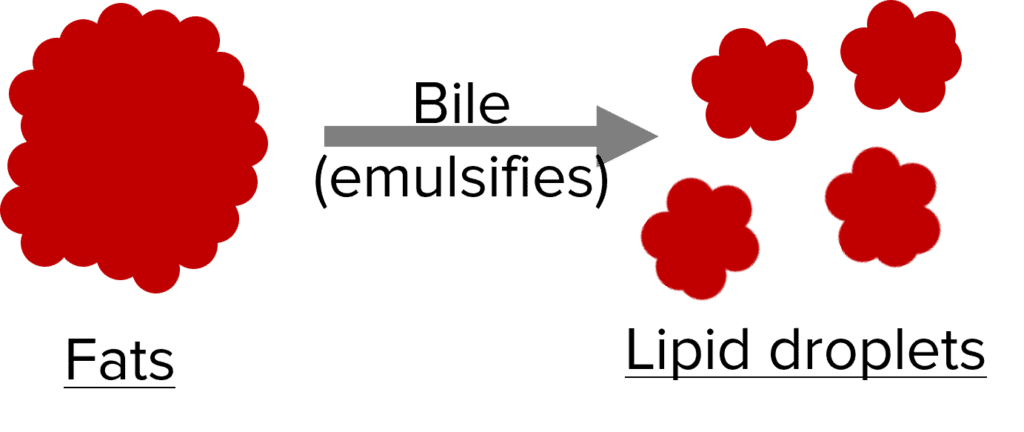
- It is an alkaline substance so neutralises hydrochloric acid from the stomach. This creates better conditions for enzymes in the small intestine so they can digest food efficiently.
- Bile also emulsifies fats which means it breaks them into small droplets. This gives them a greater surface area for lipases to work on, making digestion faster.
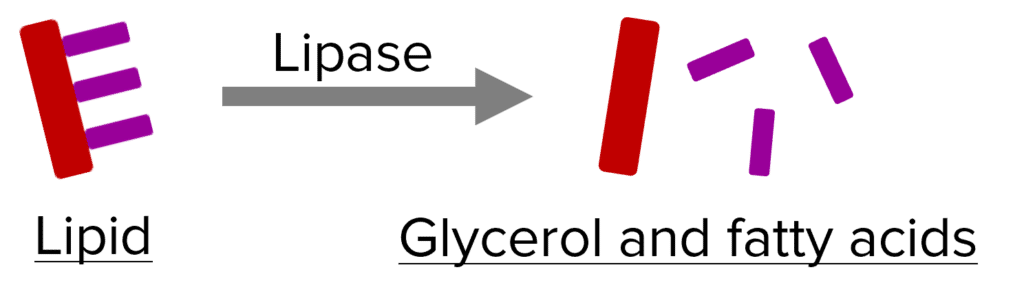
Lipases are digestive enzymes that break down lipid molecules into glycerol and fatty acids, in the small intestine. They are made in the pancreas and small intestine.
Digestive Enzymes Example Questions
Question 1: Which digestive enzyme breaks down starch and what is the main product of the reaction?
[2 marks]
Amylase breaks down starch into maltose.
Question 2: Where are proteases produced?
[3 marks]
The stomach, pancreas and small intestine.
Question 3: Name the 2 purposes of bile.
[2 marks]
Bile neutralises stomach acid and emulsifies fats.
Digestive Enzymes Worksheet and Example Questions
Enzymes Questions
GCSEOfficial MME
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now




