Disease Examples
GCSEAQABiology FoundationBiology HigherCombined Science FoundationCombined Science Higher
Disease Examples Revision
Disease Examples
Now you know about the different types of pathogens and how they are spread, you need to learn some specific disease examples.
Viral Diseases
Measles
- A highly contagious viral disease in humans that is spread between people by cough and sneeze droplets (airborne).
- Symptoms- red skin rash and fever (high temperature).
- Serious complications like pneumonia or brain inflammation can occur that can be fatal.
- No proper treatment but there is a vaccine.
- Mainly seen in children so are often vaccinated against it at an early age.
HIV
- Viral disease that can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) in humans.
- Spread through sexual contact, exchanging bodily fluids (e.g. blood exchange when drug users share needles) and from mother to baby during birth and breast milk.
- First appears as flu-like symptoms then travels to the lymph nodes to destroy cells involved in the immune response.
- Can stay hidden until the immune system is so damaged that it cannot cope with other infections and cancers (AIDS).
- Can be treated with antiretroviral drugs which slow the virus down by preventing it from attacking immune cells.
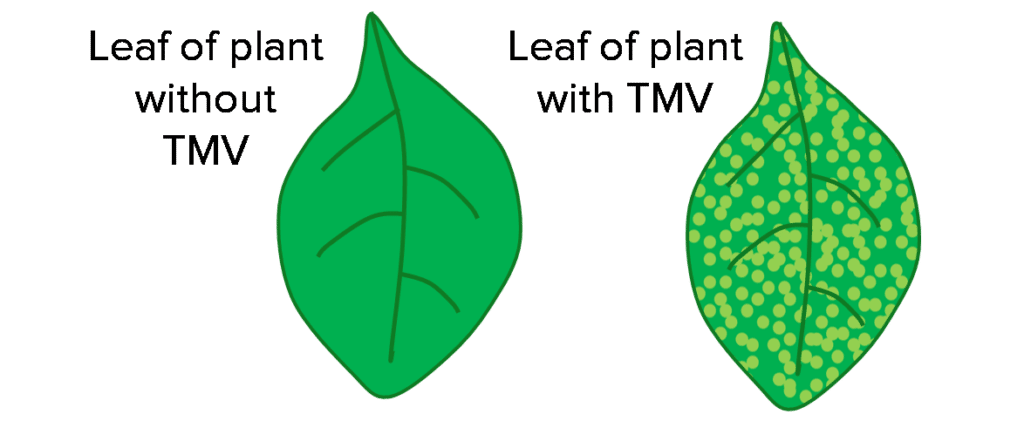

Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)
- A plant virus affecting many different species, including tomatoes.
- A distinct mosaic pattern visible on leaves.
- Discolouration of leaf limits photosynthesis and stunts growth.
GCSECombined Science FoundationCombined Science HigherBiology FoundationBiology HigherAQA
Bacterial Diseases
Salmonella
- Bacteria that causes food poisoning by releasing toxins.
- Symptoms- fever, abdominal cramps, vomiting and diarrhoea.
- Salmonella may have been acquired by the animal before it was killed for food or when the food was being prepared (if conditions were unhygienic).
- Poultry are vaccinated against salmonella (in the UK) to prevent the spread of the disease.
Gonorrhoea
- Bacterial infection spread by sexual contact (it is a sexually transmitted disease, STD).
- Symptoms- thick yellow or green discharge from the vagina or penis and pain while urinating.
- Used to be treated with the antibiotic penicillin until strains of the bacteria became resistant.
- Now, the spread of the disease is prevented using antibiotics and by encouraging people to use barrier methods such as condoms during sexual activities.
GCSECombined Science FoundationCombined Science HigherBiology FoundationBiology HigherAQA
Fungal Diseases
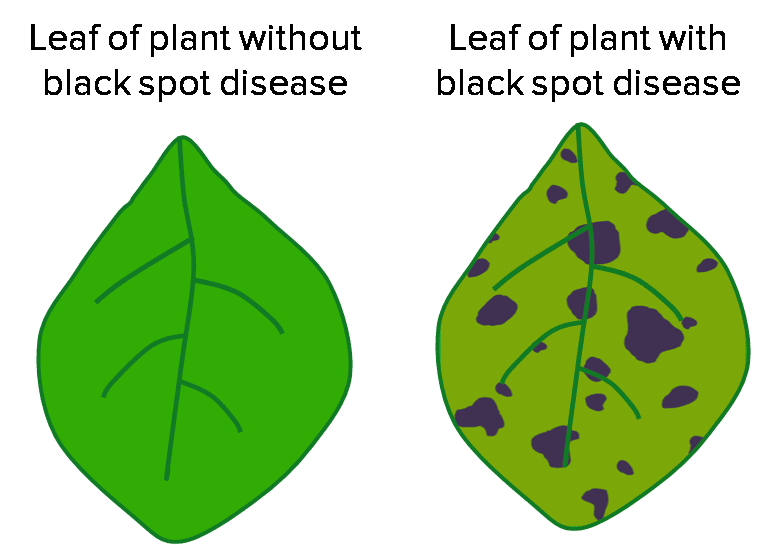

Rose Black Spot Disease
- Fungal disease affecting rose plants.
- Black or purple dots visible on leaves causing them to turn yellow and eventually drop off.
- Plant will struggle to grow because less photosynthesis can happen.
- Spread in water and wind.
- Fungicides can be used to treat the plant or infected leaves can be removed and destroyed to stop the spread.
GCSECombined Science FoundationCombined Science HigherBiology FoundationBiology HigherAQA
Protist Diseases
Malaria
- Caused by a protist that gets transported between animals by mosquitos (vector).
- The protists are picked up by mosquitos when they feed on an infected animal. They complete part of their life cycle in the mosquito vector before being transferred to another human or animal when bitten by the mosquito.
- Symptoms- repeating fever episodes that can be fatal.
- The spread of malaria can be prevented by stopping the mosquitos breeding and protecting people with mosquito nets and insecticides.
GCSECombined Science FoundationCombined Science HigherBiology FoundationBiology HigherAQA
Disease Examples Example Questions
Question 1: Describe how HIV can lead to AIDS.
[2 marks]
GCSE
Combined Science Foundation
Combined Science Higher
Biology Foundation
Biology Higher
AQA
- HIV destroys cells involved in the immune response.
- The immune system becomes so damaged it can’t cope with other infections and cancers (AIDS).
Question 2: Name one symptom of gonorrhoea and one way its spread can be prevented.
[2 marks]
GCSE
Combined Science Foundation
Combined Science Higher
Biology Foundation
Biology Higher
AQA
Symptom – Any one from:
- Thick green or yellow discharge.
- Pain while urinating.
Prevention method – Any one from:
- Use barrier methods (e.g. condoms).
- Not having sex or only having sex with uninfected people.
- Treating infected people with antibiotics.
Question 3: Name two similarities and two differences between tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) and rose black spot disease.
[4 marks]
GCSE
Combined Science Foundation
Combined Science Higher
Biology Foundation
Biology Higher
AQA
Similarities – Any two from:
- Both affect plants.
- Both cause discolouration of the leaves.
- Both prevent plant growth due to limiting photosynthesis.
Differences – Any two from:
- TMV is caused by a virus, rose black spot disease is caused by a fungus.
- TMV affects lots of different plants including tomatoes, rose black spot disease affects rose plants.
- TMV causes a mosaic pattern, rose black spot disease causes spots.






