Respiration and Exercise
Respiration and Exercise Revision
Respiration and Exercise
When we exercise the body has to adapt to meet the increased demand for oxygen. If this need is not properly met, cells start respiring anaerobically. Anaerobic respiration causes lactic acid to build up and disrupt muscle function and creates an oxygen debt. Simple investigations can show the effects of exercise on the body.
Increased Demand for Energy
During exercise, muscle cells contract more often to create movement.
Muscles require energy to contract so will need to respire more to meet the energy demand.
The body must supply the respiring cells with more oxygen for the increased respiration and also remove the carbon dioxide that is produced.
It does this in three ways:
- Increasing heart rate – increases rate of blood flow around the body.
- Increasing breathing rate– increases the rate of gas exchange in the lungs.
- Increasing breath volume– increases the rate of gas exchange in the lungs.
If the body cannot meet the increased demand for oxygen, the muscle cells must respire anaerobically.
Exercise and Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration happens in the absence of oxygen and causes the incomplete oxidation of glucose, producing lactic acid.
Lactic acid builds up in the muscles, causing them to contract less efficiently and become fatigued.
An oxygen debt is also created. This is the amount of oxygen the body needs after exercise to oxidise the lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water and remove it from the cells.
To help repay the oxygen debt and remove any remaining carbon dioxide, the heart rate and breathing rate stay high for some time after exercise.
Note:
Higher tier students should also know that some lactic acid is transported to the liver via the blood, where it is converted into glucose and then stored as glycogen.
Investigating the Effects of Exercise
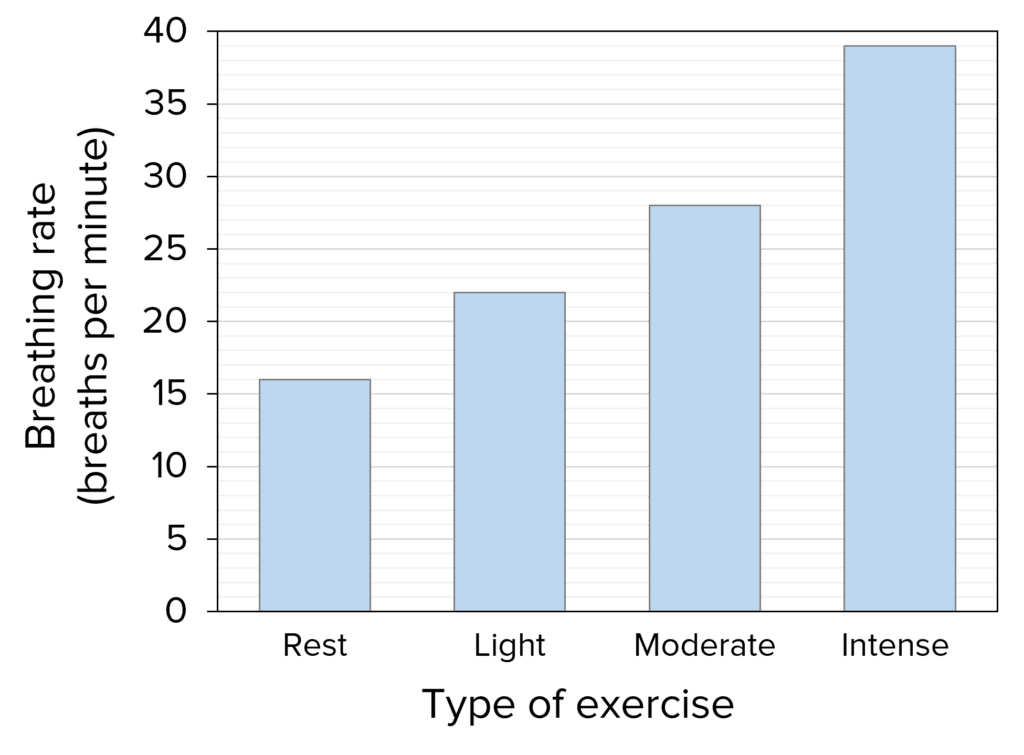
Simple investigations can be carried out to determine the effects of exercise on the body such as comparing breathing rate or heart rate before and after exercise.
Breathing rate can be calculated by counting how many breaths a person takes in a minute.
Heart rate can be calculated by measuring the pulse over a minute.
The results can then be plotted on a simple bar chart.
Monitoring breathing rate and heart rate can help determine the physical fitness of an individual.
Respiration and Exercise Example Questions
Question 1: Explain why heart rate increases when beginning exercise.
[2 marks]
When exercising, muscles contract more so will require more energy.
So they will need more oxygen for more respiration to release more energy.
Question 2: What are the consequences of lactic acid build up in muscle cells?
[2 marks]
Prevents efficient muscle contraction.
Causes muscles to become fatigued.
Question 3: Describe two ways the body removes lactic acid after exercise.
[2 marks]
- Oxidised to carbon dioxide and water.
- Converted to glucose then glycogen in the liver.






