Cosine Rule
Cosine Rule Revision
Cosine Rule
When we first learn the cosine function, we learn how to use it to find missing side-lengths & angles in right-angled triangles. The cosine rule is an equation that can help us find missing side-lengths and angles in any triangle.
Make sure you are happy with the following topics before continuing:
Cosine Rule Formula
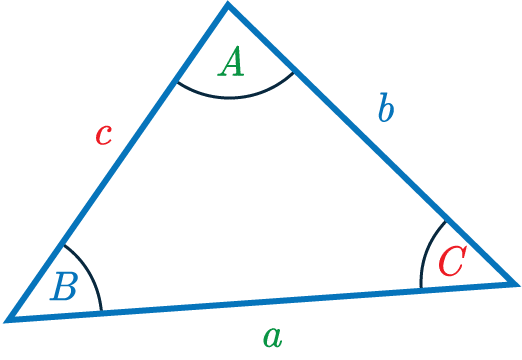
The cosine rule is an equation that helps us find missing side-lengths and angles in any triangle.
It is expressed according to the triangle on the right.
The cosine rule is
\textcolor{limegreen}{a}^2=\textcolor{blue}{b}^2+\textcolor{red}{c}^2-2\textcolor{blue}{b}\textcolor{red}{c}\cos \textcolor{limegreen}{A}
In this topic, we’ll go through examples of cosine rule questions.

Example: Cosine rule to find a length
Use the cosine rule to find the side-length marked x to 1 dp.
[3 marks]
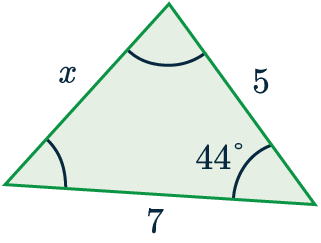
First we match up the information in the question to the letters in the formula.
a=x, A = 44\degree, b=5 and c=7.
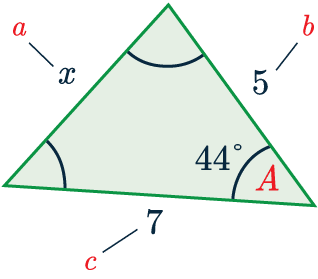
So, we’re ready to substitute the values into the formula.
x^2=5^2+7^2-(2\times5\times7\times\cos(44))=25+49-70\cos(44)
Taking the square root of both sides, and putting it into the calculator, we get
x=\sqrt{25+49-70\cos(44)}=4.9 (1 dp).
Cosine Rule Example Questions
Question 1: Use the cosine rule to find the side-length marked x below to 2 significant figures.
[3 marks]
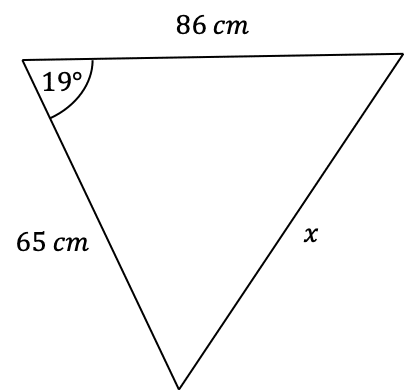
Firstly, we need appropriately label the sides of this triangle. Firstly, we set a=x, and therefore we get that A=19, since it is the angle opposite. It doesn’t matter how we label the other two sides, so here we’ll let b=86 cm and c=65 cm. Now, subbing these values into the cosine rule equation, we get
x^2=86^2+65^2-(2\times86\times65\times\cos(19\degree))=7,396+4,225-11,180\cos(19\degree)
Then, taking the square root, and putting it into the calculator, we get,
x=\sqrt{7,396+4,225-11,180\cos(19\degree)}=32 cm (2 sf).
Question 2: Use the cosine rule to find the angle marked x below to 1 decimal place.
[3 marks]
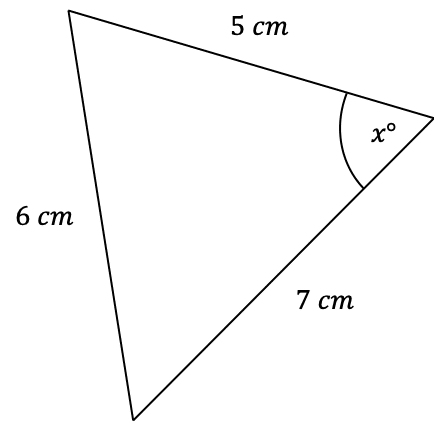
As always, we must label our triangle. Firstly, assign the thing we’re looking for to be A=x, and therefore make the side opposite to it a=6 mm. Then, it doesn’t matter how we choose the other two sides, so we will let b=5 mm and c=7 mm.
Here, we will use the rearranged version of the formula that looks like
\cos A=\dfrac{b^2+c^2-a^2}{2bc},
So, subbing these values into the equation, we get
\begin{aligned} \cos x &=\dfrac{5^2+7^2-6^2}{2\times5\times7} \\ \\ &=\dfrac{25+49-36}{70}\end{aligned}
Taking \cos^{-1} of both sides, and putting it into a calculator, we get
x=\cos^{-1}\left(\dfrac{25+49-36}{70}\right)=57.1\degree (3 sf).
Question 3: Use the cosine rule to find the side-length marked x below to 2 significant figures.
[3 marks]
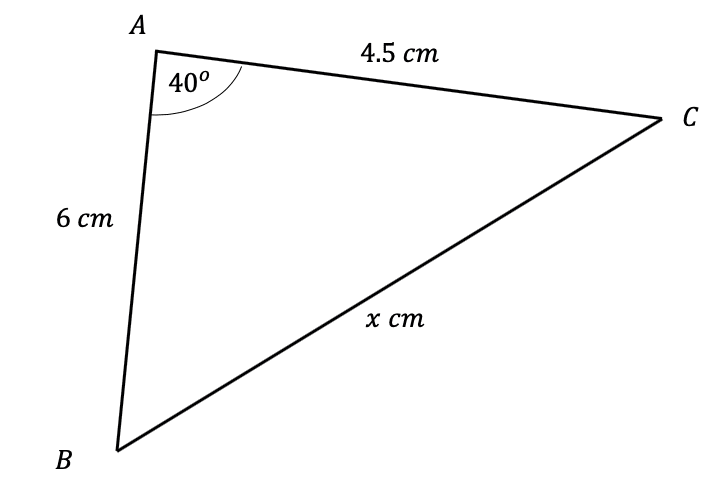
Firstly, we need appropriately label the sides of this triangle. Firstly, we set a=x, and therefore we get that A=40\degree, since it is the angle opposite. It doesn’t matter how we label the other two sides, so here we’ll let b=6 cm and c=4.5 cm. Now, substiuting these values into the cosine rule equation, we get,
x^2=6^2+4.5^2-(2\times6\times4.5\times\cos(40\degree))=36+20.25-54\cos(40\degree)
Then, taking the square root, and putting it into the calculator, we get,
x=\sqrt{56.25-54\cos(40\degree)}=3.9 cm (2 sf).
Question 4: Use the cosine rule to find the angle marked x below to 1 decimal place.
[3 marks]
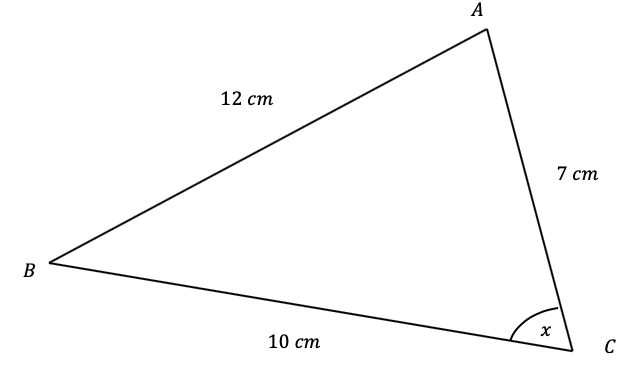
We can use the rearranged version of the formula that looks like,
\cos A=\dfrac{b^2+c^2-a^2}{2bc}
So, subbing these values into the equation, we get
\begin{aligned} \cos x &=\dfrac{7^2+10^2-12^2}{2\times7\times10} \\ \\ &=\dfrac{49+100-144}{140} \end{aligned}
Taking \cos^{-1} of both sides, and putting it into a calculator, we get
x=\cos^{-1}\left(\dfrac{5}{140}\right)=88.0\degree (1 dp).
Question 5: Use the cosine rule to find the side-length marked x below to 2 significant figures.
[3 marks]
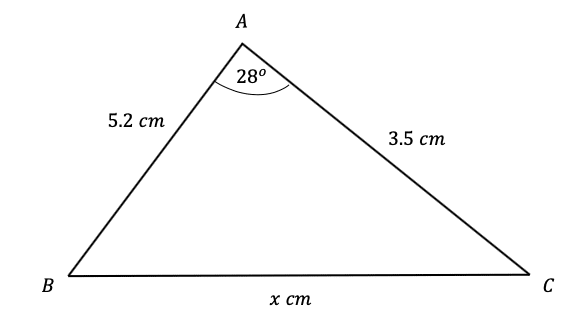
Substituting values into the cosine rule equation, we get,
x^2=5.2^2+3.5^2-(2\times5.2\times3.5\times\cos(28\degree))=27.04+12.25-36.4\cos(28\degree)
Then, taking the square root, and putting it into the calculator, we get,
x=\sqrt{39.29-36.4\cos(28\degree)}=2.7 cm (2 sf).
Cosine Rule Worksheet and Example Questions
(NEW) Cosine Rule Exam Style Questions -MME
Level 6-7GCSENewOfficial MME(NEW) Sine and Cosine rule mixed Exam Style Questions -MME
Level 6-7Level 8-9GCSENewOfficial MMECosine Rule Drill Questions
Cosine Rule - Drill Questions
Level 6-7GCSE
MME Premium Membership
£19.99
/monthLearn an entire GCSE course for maths, English and science on the most comprehensive online learning platform. With revision explainer videos & notes, practice questions, topic tests and full mock exams for each topic on every course, it’s easy to Learn and Revise with the MME Learning Portal.
Sign Up Now