Iterative Methods
Iterative Methods Revision
Iterative Methods
Iterative methods or iterations is the idea of repeating a process over and over with the purpose of getting closer to an answer. In maths, iterative methods are often used when finding an exact answer is not so simple. There are 3 key skills involved with iterative method questions at GCSE level, which are shown below.
Make sure you are happy with the following topics before moving onto Iterative methods
Skill 1: Trial and Improvement
Trial and improvement is an iterative process whereby you try different solutions for an equation until you get the degree of accuracy that you want. This is easiest to see with an example.
Example: Use trial and improvement show that \textcolor{blue}{x}^3+6\textcolor{blue}{x}=4 has a solution between 0 and 1.
Give your answer to 1 dp.
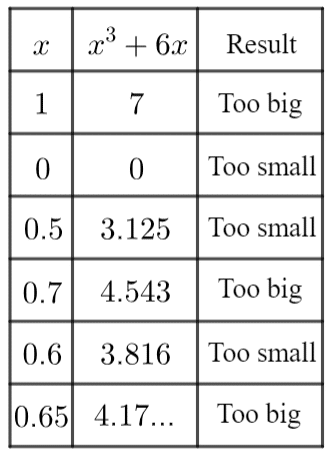

First pick the largest number in the range (\textcolor{blue}{x=1}). Then, substitute this value into the equation.
\textcolor{blue}{x}^3 +6\textcolor{blue}{x} = (\textcolor{blue}{1})^3 +6(\textcolor{blue}{1}) = 1 + 6 = 7
We know 7>4 (it’s too big), so we must try a smaller number. \textcolor{blue}{x=0}
\textcolor{blue}{x}^3+6\textcolor{blue}{x}=(\textcolor{blue}{0})^3 + 6(\textcolor{blue}{0})=0
0 is too small, so we know the solution must be somewhere in between 0 and 1.
We now repeat this process,
\begin{aligned}(\textcolor{blue}{0.5})^3 + 6(\textcolor{blue}{0.5})&=3.125.. \, \text{Too small}& \\ (\textcolor{blue}{0.7})^3 + 6(\textcolor{blue}{0.7})&=4.543..\, \text{Too big}& \\ (\textcolor{blue}{0.6})^3 + 6(\textcolor{blue}{0.6})&=3.816..\, \text{Too small}& \\ (\textcolor{blue}{0.65})^3 + 6(\textcolor{blue}{0.65})&=4.17..\,\,\,\, \text{Too big}&\end{aligned}
As we can now see, 0.6 = too small, but 0.65= too big. This means the actual solution must be between these two values.
We know that any number between 0.6 and 0.65 must round to 0.6 to 1 dp, so the solution must be 0.6 to 1dp.
Skill 2: Using Iteration Machines
An iteration machine allows us to find an approximate solution to an equation we may not be able to solve any other way.
Example: Use the iterative formula shown to find the value of x to 1 dp
\textcolor{red}{x_{n+1}} = \dfrac{4-\textcolor{limegreen}{x_{n}}^3}{6}
Use x_1 = 1.
Step 1: Use x_1 as \textcolor{limegreen}{x_n} in the equation to give \textcolor{red}{x_{x+1}}
x_1 = 1 \,\,\ \text{gives } \,\,\, \textcolor{red}{x_2} = \dfrac{4-{\textcolor{limegreen}{x_{1}}}^3}{6}=\dfrac{4-(\textcolor{limegreen}{1})^3}{6}=\textcolor{red}{0.5}
Step 2: Repeat the process using x_2 as \textcolor{limegreen}{x_n} to give \textcolor{red}{x_3}
x_2 = 0.5 \,\,\, \text{ gives } \,\,\, \textcolor{red}{x_3} = \dfrac{4-{\textcolor{limegreen}{x_{2}}}^3}{6}=\dfrac{4-(\textcolor{limegreen}{0.5})^3}{6}=\textcolor{red}{0.6548333...}
Step 3: Repeat the process to give x_4, x_5, ….
x_3=0.6548333... \,\,\, \text{ gives } \,\,\, \textcolor{red}{x_4}=\dfrac{4-{\textcolor{limegreen}{x_{3}}}^2}{6}=\dfrac{4-(\textcolor{limegreen}{0.6548333...})^3}{6}=\textcolor{red}{0.6217...}
x_4=0.6217... \,\,\, \text{ gives } \,\,\, \textcolor{red}{x_5}=\dfrac{4-{\textcolor{limegreen}{x_{4}}}^2}{6}=\dfrac{4-(\textcolor{limegreen}{0.6217...})^3}{6}=\textcolor{red}{0.6266...}
Step 4: Once two consecutive answers round to the same 1 dp answer, we have our final answer.
\xcancel{0.6548333... \,\,\, \text{rounds to} \,\,\, 0.7}
0.6217... \,\,\, \text{rounds to} \,\,\, 0.6
0.6266... \,\,\, \text{rounds to} \,\,\, 0.6
Final answer x = 0.6 (1dp)
Note: When doing a question like this, it makes your life a lot easier if you use the ANS key on your calculator.
Skill 3: Creating the iteration formula
It is often necessary to form the iterative methods formula (e.g. x_{n+1}=f(x_n)) by rearranging an equation.
Example: Show that x^3+x^2 =7 can be rearranged to give to give x_{n+1} = \sqrt[3]{7-{x_{n}}^2}
In order to do this we need to rearrange the equation to be in the form stated, then add in the notation required.
\begin{aligned} (-x^2) \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, x^3+x^2 &=7 \\ (\sqrt[3]{}) \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, x^3 &= 7-x^2 \\ x &= \sqrt[3]{7-x^2}\end{aligned}
Finally we add in the required notation to complete our answer.
\begin{aligned}x &= \sqrt[3]{7-x^2} \\ x_{n+1} &= \sqrt[3]{7-{x_{n}}^2} \end{aligned}
Iterative Methods Example Questions
Question 1: Starting with x=2, use trial and improvement to find a solution to the following equation to 1 decimal place,
2x^3-6x=1
[3 marks]
We will form a table with one column of x values, one column on the results of calculating 2x^3-6x, and one column stating if the answer is bigger or smaller than the desired 1.
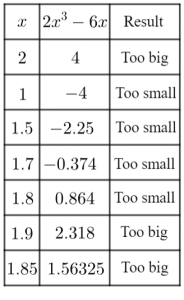
So, if 1.8 gives a result that is too small and 1.85 gives a result that is too big, then the actual solution must be somewhere between these two values.
Given that any number between 1.8 and 1.85 must round to 1.8, the solution must be 1.8 to 1 decimal place.
Question 2: Starting with x_1=2, use the iterative formula
x_{n+1}=\sqrt[3]{3x+9}
to find a solution to x^3-3x-9=0 to 2 decimal places.
[3 marks]
To find a solution we will use the recursive formula, until we get two consecutive terms which round to the same number to 2 decimal places.
\begin{aligned} x_1&=2 \\ x_2&=\sqrt[3]{3(2)+9}=2.4662 \\ x_3&=\sqrt[3]{3(2.4662)+9}=2.54060 \\ x_4&=\sqrt[3]{3(2.54060 )+9}=2.55207 \\ x_5&=\sqrt[3]{3(2.55207 )+9}=2.55383\end{aligned}
These last two results both round to 2.55 to 2dp, so the solution must be 2.55 to 2 decimal places.
Question 3: Starting with x_1=1, use the iterative formula
x_{n+1}=\dfrac{-3}{{x_{n}}^2+5}
to find a solution to x^3+5x+3=0 to 2 decimal places.
[3 marks]
To find a solution we will use the recursive formula, until we get two consecutive terms which round to the same number to 2 decimal places.
\begin{aligned}x_1&=1 \\ x_2&=\dfrac{-3}{(1)^2+5}=-0.5 \\ x_3&=\dfrac{-3}{(-0.5)^2+5}=-0.5714 \\ x_4&=\dfrac{-3}{(-0.5714 )^2+5}=-0.5632 \\ x_5&= \dfrac{-3}{(-0.5632 )^2+5}= -0.564\end{aligned}
These last two results both round to -0.56 to 2dp, so the solution must be -0.56 to 2 decimal places.
Question 4: Starting with x_1=4, use the iterative formula
x_{n+1}=\dfrac{3}{(x_n)^2}+3
to find a solution to 3x^2-x^3+3=0 to 3 decimal places.
[3 marks]
To find a solution we will use the recursive formula, until we get two consecutive terms which round to the same number to 3 decimal places.
\begin{aligned}x_1&=4 \\ x_2&=\dfrac{3}{(4)^2}+3=3.1875 \\ x_3&=\dfrac{3}{(3.1875)^2}+3=3.29527 \\ x_4&=\dfrac{3}{(3.29527)^2}+3=3.27627 \\ x_5&=\dfrac{3}{(3.27627)^2}+3=3.27949 \\ x_6&=\dfrac{3}{(3.27949)^2}+3=3.27894 \\ x_7&=\dfrac{3}{(3.27894)^2}+3=3.27903\end{aligned}
These last two results both round to 3.279 to 3dp, so the solution must be 3.279 to 3 decimal places.
Question 5: Starting with x_1=2, use the iterative formula
x_{n+1}=\sqrt[3]{6x+5}
to find a solution to x^3-6x-5=0 to 2 decimal places.
[3 marks]
To find a solution we will use the recursive formula, until we get two consecutive terms which round to the same number to 2 decimal places.
\begin{aligned} x_1&=2 \\ x_2&=\sqrt[3]{6(2)+5}= 2.57128 \\ x_3&=\sqrt[3]{6(2.57128)+5}= 2.73363 \\ x_4&=\sqrt[3]{6(2.73363)+5}= 2.77641 \\ x_5&=\sqrt[3]{6(2.77641)+5}= 2.78746 \\ x_6&=\sqrt[3]{6(2.78746)+5}= 2.79030 \\ x_7&=\sqrt[3]{6(2.79030)+5}= 2.791036\end{aligned}
These last two results both round to 2.79 to 2dp, so the solution must be 2.79 to 2 decimal places.