Circle Sectors, Segments and Arcs
Circle Sectors, Segments and Arcs Revision
Circle Sectors, Segments and Arcs
It can be useful to calculate the area and arc length of sectors and segments of circles.
Make sure you are happy with the following topics before continuing:
– Circles
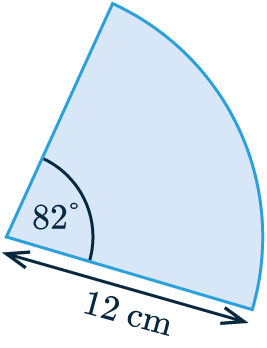
Area of a Sector
\textcolor{blue}{\text{Area of a sector}} = \dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{x}}{360} \times \textcolor{red}{\text{Area of full circle}}
Where \textcolor{limegreen}{x} is the angle of the sector.
\textcolor{red}{\text{area of the circle}} = \textcolor{red}{\pi r^2}

Calculating the area of the circle sector shown involves using the angle of the sector \textcolor{limegreen}{82} and the radius \textcolor{red}{12} cm.
We apply these to the equation above:
\dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{82}}{360} \times \textcolor{red}{\pi \times 12^2} = 103.04 \text{ cm}^2
Area of a Segment
\textcolor{blue}{\text{Area of a segment}} = \dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{x}}{360} \times \textcolor{red}{\text{Area of full circle}} - \textcolor{purple}{\text{Area of triangle}}
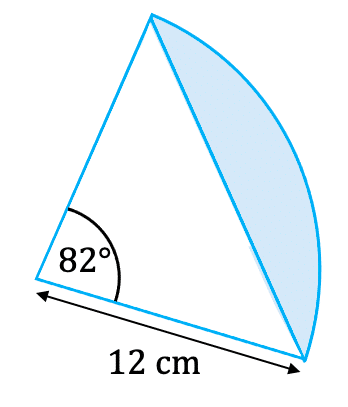

Where \textcolor{limegreen}{x} is the angle of the sector.
\textcolor{red}{\text{area of the circle}} = \textcolor{red}{\pi r^2}
\textcolor{purple}{\text{area of the triangle}} = \textcolor{purple}{\dfrac{1}{2}\,ab\, \text{sin} C}
Calculating the area of the circle segment shown involves using the angle of the sector \textcolor{limegreen}{82\degree} and the radius \textcolor{red}{12} cm.
We apply these to the equation above:
\dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{82}}{360} \times \textcolor{red}{\pi \times 12^2} - \textcolor{purple}{\dfrac{1}{2} \times 12 \times 12 \times \text{sin} 82}= 31.74 \text{ cm}^2
Click here to practice how to find the area of non-right angle triangles.
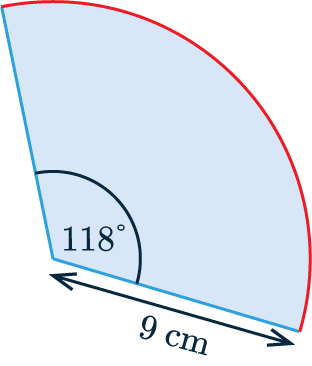
Arc Length
The arc length is the length of the part of the circumference which is part of the circle sector. The equation for this is:
\textcolor{purple}{\text{Arc Length}} = \dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{x}}{360\degree} \times \textcolor{red}{\text{circumference of full circle}}
Where \textcolor{limegreen}{x} is the angle of the sector.
\textcolor{red}{\text{Circumference of the full circle}} = \textcolor{red}{\pi D}

We can calculate the arc length of the circle sector shown by using the angle of the sector \textcolor{limegreen}{118\degree} and the diameter 2 \times\textcolor{red}{9} = \textcolor{red}{18} cm.
Now we apply these to the equation above:
\dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{118\degree}}{360\degree} \times \textcolor{red}{\pi \times 18} = 18.54 cm
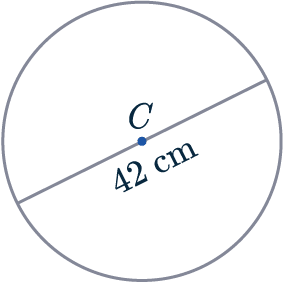
Example 1: Area and Circumference
The circle shown has centre C.
Find its area and circumference to 1 decimal place.
[2 marks]

As the line passes through the centre, we know it is a diameter of the circle. So:
Circumference = \pi d = \pi \times 42 = 131.9 \text{cm (1 dp)}
The diameter is twice the length of the radius, so the \text{radius } = 42 \div 2 = 21cm. So:
Area of circle = \pi r^2=\pi\times (21^2) = 1385.4\text{cm}^2\text{ (1 dp)}
Note: questions may ask you to “leave your answer in terms of \pi”, this means that the answer should be in the form of “something \times \pi”.
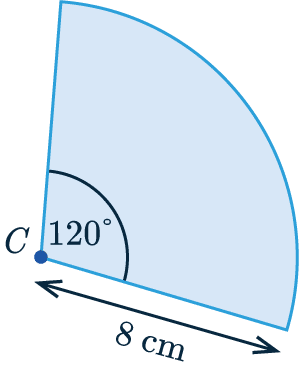
Example 2: Sector Area & Arc Length
The sector of a circle has centre C as shown.
Find the area of the sector and the arc length to 1 decimal place.
[2 marks]

The angle is 120 \degree, which means that this sector is \frac{120}{360} as a fraction of the whole circle.
So, we get:
\textcolor{blue}{\text{Sector Area}} = \dfrac{120}{360} \times \pi \times 8^2
= 67.0\text{ cm}^2 (1 dp)
\textcolor{purple}{\text{Arc Length}} = \dfrac{120}{360} \times \pi \times 2 \times 8
= 16.8\text{ cm} (1 dp)
Example 3: Segment Area
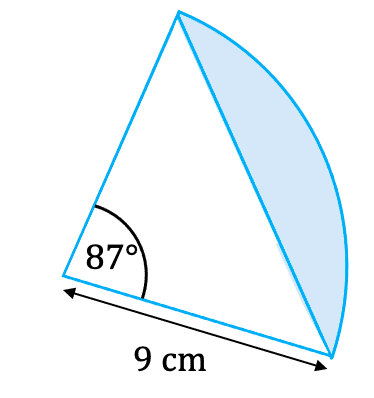

The sector of a circle has centre C as shown.
Find the area of the segment to 1 decimal place.
[2 marks]
For the question, we have a sector with an angle of 87 \degree and a radius of 9 \text{ cm}. To find the area of the segment highlighted we do the following:
\dfrac{\textcolor{limegreen}{87}}{360} \times \textcolor{red}{\pi \times 9^2} - \textcolor{purple}{\dfrac{1}{2} \times 9 \times 9 \times \text{sin} 87}= 21.1 \text{ cm}^2
Circle Sectors, Segments and Arcs Example Questions
Question 1: The diagram shows a circle with centre C.
The diameter of the circle is 5.24 cm.
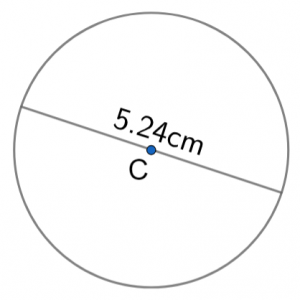
Calculate the area of the circle.
Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
[2 marks]
The formula for the area of a circle is \pi r^2. In this question we are given the diameter rather than the radius. Given that the diameter is twice the length of the radius:
\text{radius} = 5.24 \div 2 = 2.62 \text{cm}
Therefore,
\text{area } = \pi r^2 = \pi \times (2.62)^2 = 21.6 \text{cm}^2
Question 2: The diagram shows the sector of a circle with centre O.
The radius of the circle is 5 m and the angle of the sector is 72\degree.
Calculate the area of the sector.
Leave your answer in terms of \pi.
[2 marks]
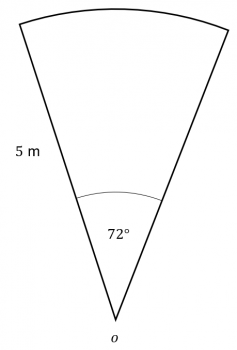
The formula for the area of a circle is \pi r^2. The area of the sector is,
\text{area} =\dfrac{72\degree}{360\degree} \times \pi (5)^2 = \dfrac{72\degree}{360\degree} \times 25 \pi = 5\pi\text{ m}^2
Question 3: The diagram shows a sector of a circle with an area of 26.15 \text{m}^2.
Calculate the value of the angle x\degree.
Give your answer to one decimal place.
[3 marks]
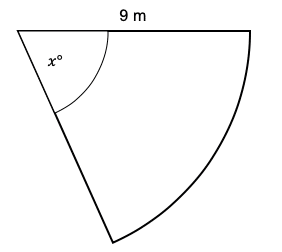
The formula for the area of a circle is \pi r^2. The area of this sector, 26.15 \text{m}^2, must be equal to \frac{x}{360} of the total area of the circle. So, as an equation, this looks like:
26.15 = \dfrac{x\degree}{360\degree} \times \pi \times 9^2
26.15=\dfrac{x\degree}{360\degree} \times 81\pi
Dividing the left-hand side and right-hand side by 81 \pi gives
\dfrac{26.15}{81\pi} = \dfrac{x\degree}{360\degree}
Then, multiply both sides by 360 to get,
x=\dfrac{26.15}{81\pi}\times 360\degree
x = 37.0\degree (to 1d.p.)
Question 4: The diagram shows a sector of a circle with centre C.
Calculate the total perimeter of the sector one decimal place.
[2 marks]
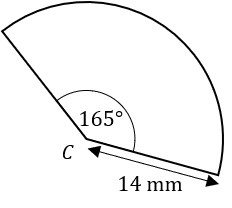
The question asks for the total perimeter of the shape. We know that one side is 14 mm but the other two are missing. Immediately we can identify that the other straight side is also 14 mm. Then, all that remains is to calculate the arc length.
The angle in this sector is 165 degrees, meaning that the arc length will be equal to \frac{165}{360} of the total circumference. The formula for the circumference is \pi d, or alternatively (and more helpfully in this case), 2\pi r. So, we get:
Arc length = \dfrac{165}{360} \times 2 \pi \times 14 = 40.3 \text{mm}
Therefore,
\text{total perimeter} = 14 + 14 + 40.3 = 68.3 \text{mm}
Question 5: The diagram shows a sector of a circle with centre C.
The area of the sector is 160\text{m}^2.
Work out the size of the missing angle to 3 significant figures.
[3 marks]
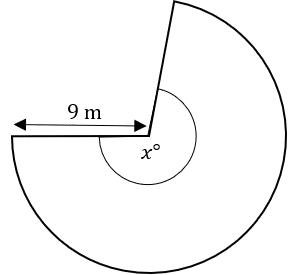
The formula for the area of a circle is \pi r^2. The area of this sector, 160 \text{m}^2, must be equal to \frac{x}{360} of the total area of the circle. So, as an equation, this looks like:
160 = \dfrac{x\degree}{360\degree} \times \pi \times 9^2
160=\dfrac{x\degree}{360\degree} \times 81\pi
Dividing the left-hand side and right-hand side by 81 \pi gives
\dfrac{160}{81\pi} = \dfrac{x\degree}{360\degree}
Then, multiply both sides by 360 to get,
x=\dfrac{160}{81\pi}\times 360\degree
x = 226\degree (to 3s.f.)
Question 6: Shown below are two circles with centres C and D
The distance between C and D is 10 \text{ cm}.
Give that \angle ADB = 120 \degree, find the area of the region where the two circles overlap.
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
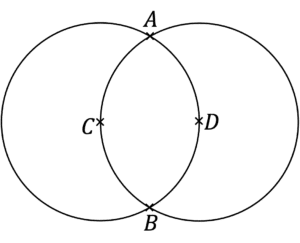
[5 marks]
Since the distance between C and D is 10 \text{ cm}, we know the radius of each circle is also 10\text{ cm}.
The region where the two circles overlap is created by two segments of equal sizes.
Area of region =2\times(\text{Area of sector} - \text{Area of triangle})
Area of region =2\times \left(\dfrac{120}{360}\times \pi \times 10^2 - \dfrac{1}{2}\times 10 \times 10 \times \text{ sin} 120 \right) = 122.84 \text{ cm}^2