Arithmetic Sequences and Sums
Arithmetic Sequences and Sums Revision
Arithmetic Sequences and Sums
An arithmetic sequence is a list of numbers, called terms. There is a common difference between consecutive terms, to for each new term the same number is added to or subtracted from the previous term. The numbers in the sequence can then be generated by a rule. We call this the nth term rule.
This rule allows us to find a value at the nth position in the sequence, which we call the nth term.
We are also able to use the nth term rule to take a sum of the first n terms of a sequence.
Finding the nth term
An arithmetic sequence is a sequence where every term has the same difference d, between it and the next term. We can use the nth term rule to generate any value in an arithmetic sequence. The rule is
The nth term = a + (n-1)d ,
where d is the common difference, and a is the very first term in the sequence.
Example: Find the 10th term in the following sequence,
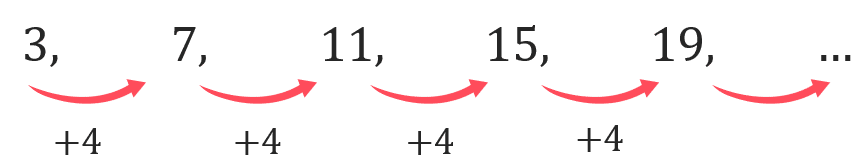
Step 1: Find the first term (a)
In this sequence the first term is given as 3.
Step 2: Find the common difference (d)
The common difference is the difference between two consecutive terms. In this case we can chose the first and second terms to find d,
d = 2\text{nd term} - 1\text{st term} = 7 - 3 = 4.
Step 3: Use the formula
a = 3, d = 4, so the 10th term is
3 + (10 - 1) \times 4 = 3 + 9\times 4 = 3 + 36 = 39
So the 10th term in the sequence is 39.
Finding the Sum of a Sequence
We can use a formula to find the sum of a sequence from the first term to the nth term, where n is the number of terms. We denote this sum as S_n
There are two formulas that can be used, although they are essentially the same.
The first formula:
S_n = \dfrac{n}{2} (2a + (n-1)d),
Where a is the first term in the sequence, n is the number of terms and d is the common difference.
From this first formula can find the second formula. We can deduce that 2a + (n-1)d = a + (a + (n-1)d) and by the nth term rule we know that the nth term = a + (n-1)d. We can call the nth term a_n and the first term a = a_1.
So 2a + (n-1)d = a_1 + a_n, which can be substituted back into the first formula.
The second formula:
S_n = \dfrac{n}{2} (a_1 + a_n)
Where a_1 is the first term, a_n is the final term, and n is the number of terms.
Example 1: Finding the 13th Term
Consider the sequence:
1, 4, 7, 10, \dots
Find the 13th term in the sequence.
[3 marks]
Firstly we can find the common difference:
2nd term - 1st term = 4 - 1 = 3
3nd term - 2st term = 7 - 4 = 3
4nd term - 3st term = 10 - 7 = 3
The common difference (d) = 3.
The first term (a) =1 .
This gives us the nth term rule of
a_n = 1 + (n-1)\times 3.
For the 13th term,
a_{13} = 1 + (13-1) \times 3
a_{13} = 1 + 12 \times 3,
a_{13} = 1 + 36,
a_{13} = 37,
The 13th term of the sequence is 37.
Example 2: Finding the sum to the 1000th term
Consider the sequence:
1, 2, 3, 4, \dots
Find the sum of the first 1000 terms in the sequence.
[3 marks]
The common difference, d = 1. The first term, a = 1
We can use the first formula for sum of an arithmetic sequence to find the sum up to n =1000.
S_{1000} = \dfrac{1000}{2} (2 \times 1 + (1000-1) \times 1)
S_{1000} = \dfrac{1000}{2} (2 + (999))
S_{1000} = \dfrac{1000}{2} (1001)
S_{1000} = 500 \times (1001)
S_{1000} = 500,500
Example 3: Determining if a value is a term in a sequence
Consider the sequence:
15, 21, 27, 33, \dots
determine whether or not the value 99 is a term in the sequence.
[3 marks]
Firstly we must find the common difference:
2nd term - 1st term = 21 - 15 = 6
3rd term - 2nd term = 27 - 21 = 6
4th term - 3rd term = 33 - 27 = 6
The common difference (d) = 6.
Therefore the nth term rule is 15 + (n - 1) \times 6
Now we can equate that to 99 to see if it is a term,
99 = 15 + (n-1) \times 6,
84 = (n-1) \times 6,
84 \div 6 = n - 1,
14 = n - 1,
n = 15,
So yes, 99 is the 15th term in the sequence.
Example 4: Using the Second Summation Formula
An arithmetic sequence has two known terms. The first term is a_1 = 7 and the 43rd term is a_{43} = 343.
Find the nth term rule and the sum of the sequence up to the 43rd term.
[4 marks]
The nth term rule:
a_n = a_1 + (n-1)d
Let n = 43 then,
a_{43} = 343 = 7 + (43 - 1)d,
343 - 7 = 42d,
336 = 42d,
336 \div 42 = d,
d = 8.
The nth term rule then is:
a_n = 7 + (n-1)\times 8
The sum to the 43rd term is:
S_{43} = \dfrac{43}{2} \times (a_1 + a_{43})
S_{43} = \dfrac{43}{2} \times (7 + 343)
S_{43} = \dfrac{43}{2} \times 350
S_{43} = 7525
Arithmetic Sequences and Sums Example Questions
Question 1: The first 5 terms of an arithmetic sequence are
3,\,\,8,\,\,13,\,\,18,\,\,23
Find the formula for the n^{th} term of this sequence.
[2 marks]
The first term, a = 3. We must now find the common difference.
2nd term - 1st term = 8 - 3 = 5.
The common difference, d = 5.
So the nth term formula is
3 + (n-1) \times 5=5n-2
Question 2: The first 5 terms of an arithmetic sequence are
-6,\,\,-4,\,\,-2,\,\,0,\,\,2
Find the sum of the first 30 terms of this sequence.
[4 marks]
The first term, a = -6. We must now find the common difference.
2nd term - 1st term = -4 - (-6) = 2 .
The common difference, d = 2.
Summation formula:
S_n = \dfrac{n}{2} (2a + (n-1)d) ,
so,
S_{30} = \dfrac{30}{2} (2 \times (-6) + (30 - 1) \times 2)
S_{30} = 15 (-12 + (29) \times 2)
S_{30} = 15 (-12 + 58) = 15 \times 46 = 690
Question 2: A sequence is defined by the formula 1080 + (n-1)(-40)
a) Work out the first 5 terms of this sequence.
[2 marks]
b) Determine whether or not -140 is in the sequence.
[2 marks]
a) To generate the first 5 terms of this sequence, we will substitute n=1, 2, 3, 4, 5 into the formula given.
1st = 1080 + ((1)-1)(-40) = 1080
2nd = 1080 + ((2)-1)(-40) = 1040
3rd = 1080 + ((3)-1)(-40) = 1000
4th = 1080 + ((4)-1)(-40) = 960
5th = 1080 + ((5)-1)(-40) = 920
So, the first 5 terms are 1080, 1040, 1000, 960, and 920
b) We can equate -140 to the nth term rule, to find it’s position in the sequence. If it’s position is a whole number, it must be in the sequence, if not it can’t be.
-140 = 1080 + (n-1)(-40)
-1220 = (n-1)(-40)
-1220 \div -40 = (n-1)
-1220 \div (-40) = 30.5 = (n-1)
n = 31.5
As n is not an integer, -140 is not in the sequence.
You May Also Like...

MME Learning Portal
Online exams, practice questions and revision videos for every GCSE level 9-1 topic! No fees, no trial period, just totally free access to the UK’s best GCSE maths revision platform.
