Interior and Exterior Angles
Interior and Exterior Angles Revision
Interior and Exterior Angles
Interior angles are the angles inside a shape.
Exterior angles are formed when a line is extended from the vertex of a shape, and are the angles between the straight line and the shape.
You need to be able to identify and calculate interior and exterior angles of shapes with many different numbers of sides.
Regular Polygons
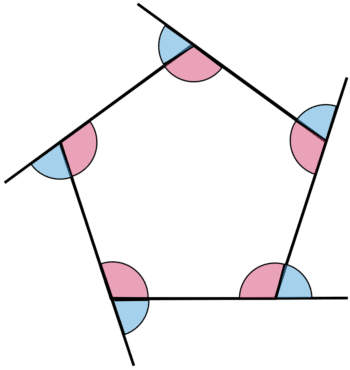
Regular polygons have equal length sides, interior angles, and exterior angles.
We can calculate interior and exterior angles when we know the number of sides the regular polygon has:
Exterior angles: \dfrac{360\degree}{\textcolor{green}{n}} where \textcolor{green}{n} is the number of sides.
Interior angles: 180\degree - exterior angle size.
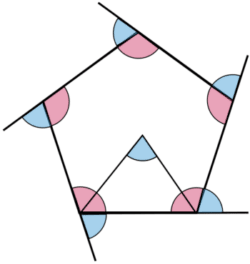
Regular polygons can also be split into several isosceles triangles, from each side to the centre of the shape. The angle in the centre is always equal to the exterior angles.
ALL polygons – Regular and Irregular
The following rules are relevant for all shapes, whether they have equal angles (regular) or different angles (irregular).
Sum of all exterior angles in a shape: 360\degree
Sum of all interior angles in a shape: (\textcolor{green}{n}-2)\times 180\degree
Example 1: Regular Polygons
Work out the size of each interior angle and each exterior angle of a regular octagon.
[4 marks]
With regular shapes, it is easiest to calculate the exterior angles first.
We can use the formula,
Exterior angle = \dfrac{360\degree}{\textcolor{green}{n}}
As we know octogons have n=8,
Exterior angle = \dfrac{360\degree}{\textcolor{green}{8}}
Exterior angle = 45\degree
Now we can calculate the size of each interior angle using,
Interior angle = 180\degree - exterior angle size
Interior angle = 180\degree - 45\degree
Interior angle = 135\degree
Example 2: Irregular Polygons
Work out the size of angle x.
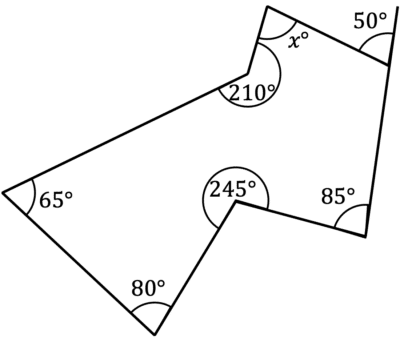
[4 marks]
By counting the sides, we can see this shape is an irregular 7 sided shape, or a heptagon.
As this shape is irregular, each angle is different, and we can use the following formula to work out the total size of the interior angles:
Sum of all interior angles = (\textcolor{green}{n}-2)\times 180\degree
Sum of all interior angles = (\textcolor{green}{7}-2)\times 180\degree
Sum of all interior angles = 900\degree
To work out angle x, we firstly need the interior angle adjacent to the exterior angle 50\degree. As these lie on a straight line, they will add to 180\degree, so the interior angle is 130\degree.
We can now calculate x:
900-130-85-245-80-65-210=85\degree
Interior and Exterior Angles Example Questions
Question 1: The image below shows a regular hexagon with centre O. Find the size of angle x.
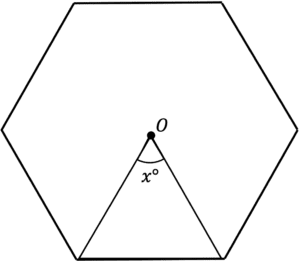
[2 marks]
We know that x will be equal to the exterior angles.
We can work out the exterior angles of a regular shape by:
\dfrac{360\degree}{n}=\dfrac{360}{6}=60\degreeQuestion 2: A regular shape has interior angles of 140\degree. Workout how many sides this shape has.
[4 marks]
If each interior angle is 140\degree, each exterior angle must be 180\degree-140\degree=40\degree.
As the shape is regular, we know that,
Exterior angle =\dfrac{360\degree}{n}
So,
40\degree=\dfrac{360\degree}{n}\\ n=\dfrac{360\degree}{40}\\ n=9Question 3: Find the angle x.
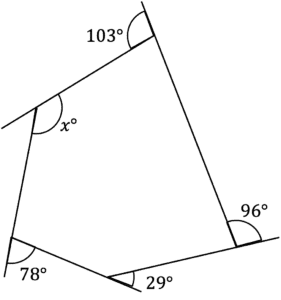
[3 marks]
It is clear that this shape is irregular, so to find x, we can firstly find the exterior angle next to x, using:
Sum of exterior angles =360\degree
360\degree-103\degree-96\degree-29\degree-78\degree=54\degreeWe can now work out the value of x:
180-54=126\degreeYou May Also Like...

MME Learning Portal
Online exams, practice questions and revision videos for every GCSE level 9-1 topic! No fees, no trial period, just totally free access to the UK’s best GCSE maths revision platform.
